An increasing number of businesses are leveraging Google Ads as a core channel for driving traffic. Not only has it revolutionized how international enterprises reach their target audience, but it also remains the most efficient way for companies to showcase their products to potential customers. However, many international businesses face various challenges when managing Google Ads campaigns. In this article, we will discuss key Google Ads performance metrics to monitor and share some valuable campaign management tips to help improve cost-effectiveness and optimize ad performance.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Ad Performance
Google Ads performance metrics are essential for any marketing campaign. They can help assess the success of your ads as well as serve as crucial data for future optimization. So, what core data should you focus on when evaluating your Google Ads campaigns?

- Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR measures how many people clicked on your ad from those who saw it. This metric helps you gauge the effectiveness of your ad’s appeal and relevance.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): CPC is the cost incurred for each click on your ad. It indicates how much you pay to drive traffic to your website, calculated based on the number of clicks your ad receives.
- Conversion Rate (CVR): CVR tracks the percentage of ad clicks that result in conversions, providing insight into how effectively your ad drives desired actions, such as purchases or sign-ups.
- Cost Per Action (CPA): CPA measures the cost of each specified action that a user takes after clicking your ad. This pricing model charges you based on the actions users take, making it a key metric for evaluating the efficiency of your ad spend.
Industry Differences in Google Ads Performance Metrics
1. Cost Per Click (CPC)
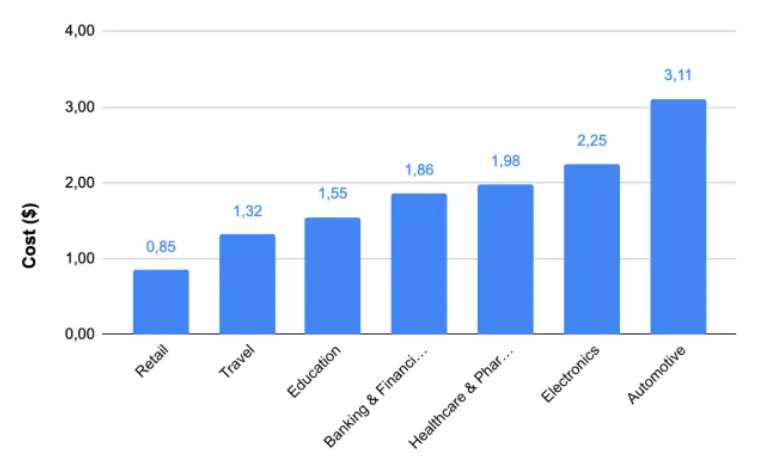
The cost per click for Google Shopping ads varies significantly across different industries, influenced by factors such as keyword competition and ad quality. As illustrated below, the automotive industry has the highest CPC at $3.11 per click, whereas the retail industry has the lowest CPC at $0.85 per click.
2. Conversion Rate (CVR)
Conversion rates vary widely across different industries. As shown below, the average CVR for retail and electronics is 2.19% and 2.41%, respectively. The education and automotive sectors see higher conversion rates at 3.12% and 4.95%. The banking and financial services industry boasts the highest conversion rate at 4.50%.

3. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
The click-through rate for Google Shopping ads indicates the effectiveness of your ads, influenced by factors such as ad copy, targeting, and bidding. As shown below, the automotive industry has the highest CTR at 5.02% due to high competition. Conversely, the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries have the lowest CTR at 2.67%, likely due to the sensitive nature of their products and services.

4. Cost Per Action (CPA)
CPA is primarily influenced by factors such as ad quality and targeting. Optimizing your marketing campaigns and improving these elements can help reduce CPA. The average CPA on the Google Search Network is $56.11, ranging from $31.27 for the retail industry to $54.40 for the automotive industry, as shown below.

Understanding these industry-specific variations in key metrics allows businesses to effectively utilize them, providing a crucial reference for scientifically planning international advertising campaigns.
How to Effectively Utilize Google Ads Performance Metrics
Evaluating the effectiveness of Google Ads requires not only monitoring multiple metrics but also considering their interrelationships. When selecting keywords, formulating ad strategies, and optimizing ad content, it’s essential to develop corresponding strategies based on different metrics. Here’s how to do it:

1. Compare Campaign Metrics with Industry Averages
People can quickly identify whether their ads are underperforming compared to competitors by comparing and analyzing Google Ads metrics within the industry. For example, if a business’s Google Ads conversion rate is below the vertical industry average, modifications to ad targeting or ad copy can be made to improve conversion rates.
2. Identify and Improve Weak Areas in Ads
Regularly review your ad campaigns to quickly pinpoint weak areas and make timely improvements. For instance, if your ad’s click-through rate (CTR) is significantly low, investigate the ad copy and extensions to identify areas for improvement. Enhancing these aspects can boost the CTR, resulting in more clicks and conversions.

3. Track Industry Trends and Empower Decision-Making
By analyzing data, you can quickly identify emerging industry trends that inform promotional decisions, including targeting, budget allocation, and campaign strategies. For example, if competitors are investing heavily in a particular ad format or channel, you can use this as a reference to explore new business opportunities and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Final Thoughts
Advertising requires continuous refinement and expertise. It is crucial to continually enhance skills and stay informed about industry best practices. To achieve the best results, companies should consider building a specialized team or hiring professionals to manage Google Ads campaigns, ultimately driving better performance and results.




